Union Budget 2023 highlights
Union Budget 2023 highlights

Why in news? Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented her fifth budget and first Budget of Amrit Kaal.
Introduction:
- This Budget hopes to build on the foundation laid in the previous Budget, and the blueprint drawn for India@100.
- current year’s economic growth is estimated to be at 7 per cent. It is notable that this is the highest among all the major economies.
- India’s rising global 2 profile is because of several accomplishments: unique world class digital public infrastructure, e.g., Aadhaar, Co-Win and UPI; Covid vaccination drive in unparalleled scale and speed; proactive role in frontier areas such as achieving the climate related goals, mission LiFE, and National Hydrogen Mission.
- to ensure food and nutritional security, government is implementing, from 1st January 2023, a scheme to supply free food grain to all Antyodaya and priority households for the next one year, under PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY). The entire expenditure of about ` 2 lakh crore will be borne by the Central Government.
- The efficient implementation of many schemes, with universalisation of targeted benefits, has resulted in inclusive development. Some of the schemes are:
- Swachh Bharat Mission,
- LPG connections under Ujjawala,
- Covid vaccination of 102 crore persons,
- PM Jan Dhan bank accounts,
- Insurance cover for 44.6 crore persons under PM Suraksha Bima and PM Jeevan Jyoti Yojana,
- Cash transfer of ` 2.2 lakh crore to over 11.4 crore farmers under PM Kisan Samman Nidhi.
Vision for Amrit Kaal – an empowered and inclusive economy
- Includes technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with strong public finances, and a robust financial sector.
The following four opportunities can be transformative during Amrit Kaal.
1) Economic Empowerment of Women
2) PM VIshwakarma KAushal Samman (PM VIKAS)
3) Tourism:
4) Green Growth
Priorities of this Budget
- The Budget adopts the following seven priorities. They complement each other and act as the ‘Saptarishi’
- inclusive development,
- infrastructure and investment,
- reaching the last mile,
- unleashing the potential,
- green growth,
- youth power
- financial sector.
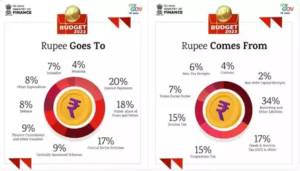
Defence budget
- Defence budget rises 13%
- The hike is particularly significant given the huge increase in operational commitments, with major force accretion and sustenance along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), and stocking up of spares and ammunition since the 2020stand-off with China.
Department of Space
- The expenditure of the Department of Space has been slashed by 8% in the 2023-24
- Expenditure for space science, that includes the ISRO science missions such as Chandrayaan 3, Aditya L1, and its Climate and Atmospheric Programme, has received a nominal cut of from the previous budget estimate
Priority 1: Inclusive Development
- inclusive development covers in specific, farmers, women, youth, OBCs, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, divyangjan and economically weaker sections, and overall priority for the underprivileged
- There has also been a sustained focus on Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh and the North-East
Agriculture and Cooperation
- Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Agriculture Accelerator Fund
- Enhancing productivity of cotton crop
- Atmanirbhar Horticulture Clean Plant Program
- Global Hub for Millets: ‘Shree Anna’
- Agriculture Credit
- Fisheries: PM Matsya Sampada Yojana
- Cooperation
Health, Education and Skilling
- Nursing Colleges
- Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission
- Medical Research
- Pharma Innovation
- Multidisciplinary courses for medical devices
- Teachers’ Training
- National Digital Library for Children and Adolescents
Priority 2: Reaching the Last Mile
- To provide a sharper focus to the objective of ‘reaching the last mile’, government has formed the ministries of AYUSH, Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Skill Development, Jal Shakti and Cooperation.
Programmes undertaken:
- Aspirational Districts and Blocks Programme
- Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools
- Water for Drought Prone Region
- PM Awas Yojana: The outlay for PM Awas Yojana has been increased by 66% to over ₹79,000 crores.
- Bharat Shared Repository of Inscriptions (Bharat SHRI): a digital epigraphy museum at Hyderabad by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Support for poor prisoners
Priority 3: Infrastructure & Investment
Investments in Infrastructure and productive capacity have a large multiplier impact on growth and employment.
Programmes:
- Capital Investment as driver of growth and jobs
- Effective Capital Expenditure
- Support to State Governments for Capital Investment
- Enhancing opportunities for private investment in Infrastructure
- Harmonized Master List of Infrastructure
- Railways
- Logistics : One hundred critical transport infrastructure projects, for last and first mile connectivity for ports, coal, steel, fertilizer, and food grains sectors have been identified
- Regional Connectivity: Fifty additional airports, heliports, water aerodromes and advance landing grounds
- Sustainable Cities of Tomorrow: efficient use of land resources, adequate resources for urban infrastructure, transit-oriented development, enhanced availability and affordability of urban land, and opportunities for all
- Making Cities ready for Municipal Bonds: Through property tax governance reforms and ring-fencing user charges on urban infrastructure, cities will be incentivized to improve their credit worthiness for municipal bonds.
- Urban Infrastructure Development Fund: established through use of priority sector lending shortfall. This will be managed by the National Housing Bank, and will be used by public agencies to create urban infrastructure in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- Urban Sanitation
Priority 4: Unleashing the Potential
- Mission Karmayogi
- the Jan Vishwas Bill
- Centres of Excellence for Artificial Intelligence: For realizing the vision of “Make AI in India and Make AI work for India”, three centres of excellence for Artificial Intelligence will be set-up in top educational institutions.
- National Data Governance Policy
- Simplification of Know Your Customer (KYC) process

- Common Business Identifier: the PAN will be used as the common identifier for all digital systems of specified government agencies. This will bring ease of doing business; and it will be facilitated through a legal mandate.
- Unified Filing Process
- Vivad se Vishwas I – Relief for MSMEs
- Vivad se Vishwas II – Settling Contractual Disputes
- State Support Mission
- Result Based Financing
- E-Courts
- Fintech Services: Fintech services in India have been facilitated by our digital public infrastructure including Aadhaar, PM Jan Dhan Yojana, Video KYC, India Stack and UPI.
- Entity DigiLocker: An Entity DigiLocker will be set up for use by MSMEs, large business and charitable trusts. This will be towards storing and sharing documents online securely, whenever needed, with various authorities, regulators, banks and other business entities.
- 5G Services
- Lab Grown Diamonds: is a technology-and innovation-driven emerging sector with high employment potential. These environmentfriendly diamonds which have optically and chemically the same properties as natural diamonds. To encourage indigenous production of LGD seeds and machines and to reduce import dependency, a research and development grant will be provided to one of the IITs for five years.
Priority 5: Green Growth
India is moving forward firmly for the ‘panchamrit’ and net-zero carbon emission by 2070 to usher in green industrial and economic transition.
- Green Hydrogen Mission
- Energy Transition
- Energy Storage Projects
- Renewable Energy Evacuation
- Green Credit Programme: For encouraging behavioural change, a Green Credit Programme will be notified under the Environment (Protection) Act. This will incentivize environmentally sustainable and responsive actions by companies, individuals and local bodies, and help mobilize additional resources for such activities.
- PM-PRANAM:“PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother Earth” will be launched to incentivize States and Union Territories to promote alternative fertilizers and balanced use of chemical fertilizers.
- GOBARdhan scheme: 500 new ‘waste to wealth’ plants under GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) scheme will be established for promoting circular economy. These will include 200 compressed biogas (CBG) plants, including 75 plants in urban areas, and 300 community or cluster-based plants at total investment of ` 10,000 crore. a 5 per cent CBG mandate will be introduced for all organizations marketing natural and bio gas.
- Bhartiya Prakritik Kheti Bio-Input Resource Centres
MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes)
- It is a new programme that will facilitate mangrove plantation along India’s coastline and on salt pan lands. The programme will operate through “convergence between MGNREGS, Campa Fund and other sources
- This new programme will aim at intensive afforestation of coastal mangrove forests. India has such forests on both its Eastern and Western coasts with the Sundarbans in Bengal being one of the largest mangrove forests on the planet.
Why does this matter?
- Mangroves are not just some of the most bio-diverse locations in India, they also protect the coastlines from the vagaries of inclement weather. As climate change increases the incidence of extreme weather events across the world, mangrove plantations have shown to make coastal lands resilient, preventing flooding, land erosion and acting as a buffer for cyclones.
- Furthermore, they are also excellent carbon sinks. Mangrove trees can grow in saline waters, and can sequester up to four times more carbon than tropical rainforests.
Amrit Dharohar:
- a scheme that will be implemented over the next three years to encourage optimal use of wetlands, and enhance bio-diversity, carbon stock, eco-tourism opportunities and income generation for local communities.
- Coastal Shipping
- Vehicle Replacement:
Priority 6: Youth Power
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0: to skill lakhs of youth within the next three years. On-job training, industry partnership, and alignment of courses with needs of industry will be emphasized. The scheme will also cover new age courses for Industry 4.0 like coding, AI, robotics, mechatronics, IOT, 3D printing, drones, and soft skills. To skill youth for international opportunities, 30 Skill India International Centres will be set up across different States.
- Skill India Digital Platform
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme
- Tourism : 50 new tourist destinations will be developed and an information-driven app created for tourists that provide tourist-friendly information like physical and virtual connectivity, and details on tourist guides, among others
- Under Vibrant Villages Programme, tourism infrastructure and amenities will be facilitated in border villages.
- Unity Malls will be set up in State capitals to showcase handicrafts and products with geographical indication (GI) status.
Priority 7: Financial Sector
- Credit Guarantee for MSMEs
- National Financial Information Registry: will be set up to serve as the central repository of financial and ancillary information. This will facilitate efficient flow of credit, promote financial inclusion, and foster financial stability. A new legislative framework will govern this credit public infrastructure, and it will be designed in consultation with the RBI.
- Financial Sector Regulations
- GIFT IFSC

- Data Embassy
- Improving Governance and Investor Protection in Banking Sector
- Capacity Building in Securities Market
- Central Data Processing Centre
- Digital Payments
- Mahila Samman Savings Certificate: a one-time new small savings scheme, Mahila Samman Savings Certificate, will be made available for a two-year period up to March 2025. This will offer deposit facility upto ` 2 lakh in the name of women or girls for a tenor of 2 years at fixed interest rate of 7.5 per cent with partial withdrawal option
- Senior Citizens: The maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Savings Scheme will be enhanced from ` 15 lakh to ` 30 lakh. The maximum deposit limit for Monthly Income Account Scheme will be enhanced from ` 4.5 lakh to ` 9 lakh for single account and from ` 9 lakh to ` 15 lakh for joint account.
- Fiscal Management: Fifty-year interest free loan to States
PART B
Indirect Taxes
- Indirect tax proposals aim to promote exports, boost domestic manufacturing, enhance domestic value addition, encourage green energy and mobility.
- A simplified tax structure with fewer tax rates helps in reducing compliance burden and improving tax administration.
Green Mobility
- To avoid cascading of taxes on blended compressed natural gas, excise duty on GST-paid compressed bio gas contained in it is exempted
- To further provide impetus to green mobility, customs duty exemption is being extended to import of capital goods and machinery required for manufacture of lithium-ion cells for batteries used in electric vehicles.
Electronics:
- relief in customs duty on import of certain parts and inputs like camera lens is provided and the concessional duty on lithium-ion cells for batteries for another year is continued
- to promote value addition in manufacture of televisions, the basic customs duty on parts of open cells of TV panels is reduced to 2.5 per cent.
Electrical:
- To encourage manufacturing of electric kitchen chimneys, the basic customs duty on electric kitchen chimney is being increased from 7.5 per cent to 15 per cent and that on heat coils for these is proposed to be reduced from 20 per cent to 15 per cent.
Chemicals and Petrochemicals:
- Denatured ethyl alcohol is used in chemical industry. basic customs duty on it will be exempted . This will also support the Ethanol Blending Programme and facilitate endeavour for energy transition. Basic customs duty is also being reduced on acid grade fluorspar from 5 per cent to 2.5 per cent to make the domestic fluorochemicals industry competitive. Further, the basic customs duty on crude glycerin for use in manufacture of epicholorhydrin is proposed to be reduced from 7.5 per cent to 2.5 per cent.
Silver and silver jewellery
- Government announced increasing the basic customs duty (BCD) on silver, both in dore and semi-manufactured form, to 10% to curb imports.
Cigarettes :
- National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) on specified cigarettes was last revised three years ago. This is proposed to be revised upwards by about 16 per cent.
Direct Taxes
MSMEs and Professionals
- MSMEs are growth engines of our economy. Micro enterprises with turnover up to ` 2 crore and certain professionals with turnover of up to ` 50 lakh can avail the benefit of presumptive taxation. It is provided for enhanced limits of ` 3 crore and ` 75 lakh respectively, to the tax payers whose cash receipts are no more than 5 per cent
Cooperation
- new co-operatives that commence manufacturing activities till 31.3.2024 shall get the benefit of a lower tax rate of 15 per cent, as is presently available to new manufacturing companies.
- sugar co-operatives to claim payments made to sugarcane farmers for the period prior to assessment year 2016-17 as expenditure
- a higher limit of ` 2 lakh per member for cash deposits to and loans in cash by Primary Agricultural Co-operative Societies (PACS) and Primary Co-operative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks (PCARDBs).
- a higher limit of ` 3 crore for TDS on cash withdrawal is being provided to co-operative societies.
Other major proposals in the Finance Bill relate to the following:
- Extension of period of tax benefits to funds relocating to IFSC, GIFT
- City till 31.03.2025;
- Decriminalisation under section 276A of the Income Tax Act;
- Allowing carry forward of losses on strategic disinvestment including that of IDBI Bank;
- Providing EEE status to Agniveer Fund.
New Tax Regime
- It was announced that those earning up to 7 lakh a year need not pay any income tax under the new tax regime, giving a push for the regime which disallows all exemptions on investments
The new tax rates are:
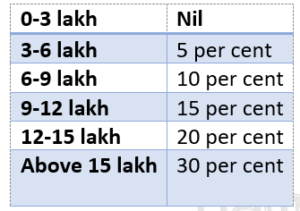
- Taxpayers can still opt to file under the old regime, that allows for tax exemptions and deductions on investments and expenses such as HRA (house rent allowance).
- Those switching to the new tax regime can also hereafter avail themselves of the 50,000 standard deduction
- regarding the highest tax rate which in our country is 42.74 per cent. This is among the highest in the world. The budget reduces the highest surcharge rate from 37
per cent to 25 per cent in the new tax regime. This would result in reduction of the maximum tax rate to 39 per cent.

