Published on: March 14, 2023
ESG (Environment, Social, and Governance) in INDIA
ESG (Environment, Social, and Governance) in INDIA

Context : The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), responding to the increase in ESG investing and the demand by investors for information on environmental, social and governance risks, substantially revised the annual Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) required by the 1,000 largest listed companies in India
What is ESG ?
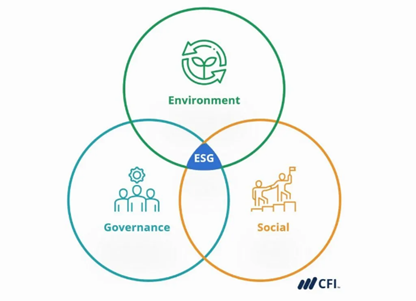
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) refer to the three key factors that organizations consider to measure their overall sustainability and societal impact
- Environmental factors pertain to the management of a company’s impact on the natural environment, such as energy use, emissions, waste management, and resource depletion. Environmental factors also take into account the organization’s efforts to promote sustainability and reduce carbon footprint
- Social factors refer to the organization’s relationship with stakeholders, such as customers, employees, suppliers, and communities. This involves the management of social risks and opportunities, including labor practices, human rights, diversity and inclusion, community engagement, and supply chain management
- Governance factors relate to the company’s internal management structures, decision-making processes, and accountability mechanisms. This includes issues such as board composition and independence, executive compensation, and financial transparency
- WHY IS IT NECESSARY –
- Integration of ESG factors into business operations and decision-making helps
- Promote responsible corporate behavior and long-term value creation
- Mitigate potential risks and enhance opportunities for sustainable growth
CSR in India
- India has a robust corporate social responsibility (CSR) policy that mandates that corporations engage in initiatives that contribute to the welfare of society .
- CSR mandate was codified into law with the passage of the 2014 and 2021 amendments to the Companies Act of 2013.
- The amendments require companies with a net worth of Rs500 crore or a minimum turnover of 1,000 crore or a net profit of Rs.5 crore in any given financial year spend at least 2% of their net profit over the preceding three years on CSR activities.
- The list of qualifying CSR activities is intentionally broad, ranging from supporting the protection of historically important sites to promoting safe drinking water.
What is the difference between CSR & ESG
- CSR initiatives are determined and demonstrated in your organization’s internal culture and policies, while ESG is an external assessment of your organization’s impact on society.
Why is ESG relevant in India?
- National Green Tribunal provides important environmental and social safeguards for establishing guidelines to emphasise monitoring, quantification and disclosure to ESG requirements found in other parts of the world.
- SEBI evolving with global standards to allow companies to engage meaningfully with stakeholders and to enhance investor decision making.
- Companies are taking intiatives with much focused on range from greenhouse gas emissions to the company’s gender and social diversity.
- Indian government on ESG issues, can be seen in India’s more active role in global climate forums as well as in specific policy developments, such as the RBI auctioning Rs80 billion in green bonds.

