Published on: November 26, 2022
China-Qatar energy deal
China-Qatar energy deal

Why in news?
China signed a 27-year deal for LNG supply with the tiny gulf monarchy, probably the longest in terms of duration in the history of LNG.
Highlights
- It is the second deal between China and a major Persian Gulf energy
- Qatar, one of the world’s tiniest countries in the Middle East, is the world’s largest Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) exporter.
- The agreement provided an impetus for China and Iran to deepen their strategic partnership. It helped that both share an anti-American strategic outlook.
- Provides a sound rationale for China to expand its regional economic and military presence in gulf region
- North Field is at the centre of Qatar’s expansion of its liquefied natural gas production
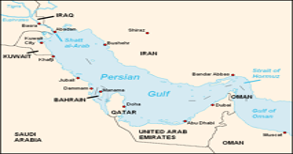
Persian Gulf
- It is a Mediterranean sea in Western Asia.
- Extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula
- It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz.
- The Shatt al-Arab river delta forms the northwest shoreline.
- The Persian Gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive reefs (mostly rocky, but also coral), and abundant pearl oysters, but its ecology has been damaged by industrialization and oil spills.
- Cenozoic origin and related to the subduction of the Arabian Plate under the Zagros Mountains
- Primary inflows: Gulf of Oman
- Basin countries : Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, United Arab Emirates and Oman
North field/ South Pars/North Dome Gas-Condensate field
- It is a natural-gas condensate field located in the Persian Gulf.
- It is by far the world’s largest natural gas field
- Ownership of the field : Shared between Iran and Qatar.

