Published on: April 6, 2023
NATO
NATO
Why in news? Finland joined the NATO military alliance, dealing a major blow to Russia with a historic realignment of the continent triggered by Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine.
Highlights:
- In joining Nato
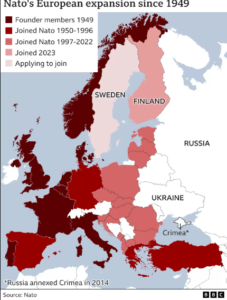 , Finland is ending seven decades as a non-aligned country.
, Finland is ending seven decades as a non-aligned country. - Finland shares a long border with Russia and applied to join the defensive alliance soon after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
What is NATO?
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization was formed in 1949 by 12 countries, including the US, UK, Canada and France.
- It is an intergovernmental military alliance between 31 member states – 29 European and two North American.
- Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C.
- Finland is the 31st country to join.
- Nato members agree to help one another if they come under attack.
- The organisation’s original goal was to challenge Soviet expansion in Europe after World War Two.
- After the Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991, many of the Eastern European countries which used to be its allies in the Warsaw Pact were granted Nato membership.
- Russia (which was formerly part of the Soviet Union) has long argued that NATO’s acceptance of Eastern European countries threatens its security.
- It has vehemently opposed Ukraine’s request to join the alliance, fearing this would encroach too closely on its territory
Why is Finland joining Nato?
- Finland shares a 1,340km land border with Russia.
- In 1948, it agreed to be a neutral country as part of a “friendship agreement” with the Soviet Union.
- When the Soviet Union collapsed, it edged closer to Nato, becoming an “official partner” of the bloc in 1994.
- Soon after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, both Finland and Sweden asked to be given full entry to Nato as soon as possible.
What hurdles did Finland face in joining Nato?
- All the parliaments of Nato member states have to agree to a new country joining the alliance.
- Finland and Sweden applied to join Nato together, but Turkey and Hungary have not yet approved Sweden’s entry.
- They were the last two member states to approve Finland’s membership as well, Turkey.
- Turkey’s government had delayed allowing Finland to join, complaining that it supported “Kurdish terrorists”.
- It is still blocking Sweden’s membership, accusing it also of harbouring Turkey’s enemies and allowing anti-Turkish demonstrations on its streets.
How are Nato countries supporting Ukraine?
- Many of the alliance’s member states have provided Ukraine with weapons and ammunition to help it defend itself against Russia.
- The US is sending 31 Abrams tanks, the UK 14 Challenger 2 tanks, Germany 14 Leopard 2 tanks and Norway eight Leopard 2 tanks.
- The US has also sent armoured fighting vehicles such as the Stryker and the Bradley.
- In addition, the US and UK have sent Ukraine long-range missile systems such as Himars, which have been striking targets behind Russia’s front lines.
- Several Nato countries have provided howitzers and self-propelled guns, while Turkey has sold Ukraine several Bayraktar TB2 drones.
- The US and others have supplied air defence systems to shoot down Russian cruise missiles and drones over Ukraine.
- The anti-tank weapons that the US and UK have supplied, such as Javelin and Nlaw, were crucial in turning back Russia’s advance on Ukraine’s capital, Kyiv, in spring 2022.
- Nato countries are also aiming to ramp up their supplies of artillery shells and ammunition to Ukraine.
Why won’t Nato countries give more help to Ukraine?
- Nato countries also fear that if Ukraine were to use these jets to strike targets inside Russia, it could draw them deeper into the war.
- Nato countries are not sending their troops to Ukraine, or imposing a no-fly zone over the country, again for fear of provoking a direct conflict with Russia.
Why isn’t Ukraine in Nato?
- Nato told Ukraine in 2008 that it could join the bloc at some point in the future, but declined its recent request for “fast-track” membership.
- Blocking because it is Article 5 of the Nato charter says that if one member is attacked, all members should come to its defence.
- If Ukraine was made a member, Nato countries would technically have to go to war with Russia.

