Published on: May 7, 2024
CARBON FARMING
CARBON FARMING
DEFENITION: Carbon farming refers to the practice of implementing regenerative agricultural techniques that enhance carbon storage in agricultural landscapes and reduce greenhouse gas emissions
CARBON’S ROLE
- Found in all living organisms and many minerals.
- Crucial for life on Earth.
- Plays a key role in photosynthesis, respiration, and the carbon cycle.
FARMING DEFINITION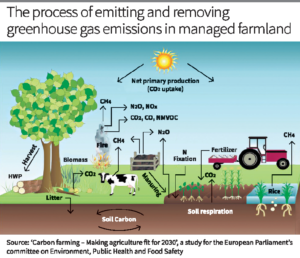
- Involves cultivating land.
- Includes raising crops and/or livestock.
- Provides food, fibre, fuel, and other resources.
- Encompasses activities like planting, harvesting, livestock management, and infrastructure maintenance.
CARBON FARMING OVERVIEW
- Combines carbon’s importance with farming practices.
- Implements regenerative techniques.
- Aims to restore ecosystem health.
- Improves agricultural productivity and soil health.
- Mitigates climate change by enhancing carbon storage and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
CARBON FARMING TECHNIQUES
- Rotational Grazing: Involves rotating livestock through different pastures to prevent overgrazing and promote soil health.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs with crops to sequester carbon and diversify farm income.
- Conservation Agriculture: Includes zero tillage, crop rotation, cover cropping, and managing crop residues to minimize soil disturbance and enhance organic content.
- Integrated Nutrient Management: Using organic fertilizers and compost to promote soil fertility and reduce emissions.
- Agro-Ecology: Encouraging crop diversification and intercropping for ecosystem resilience.
- Livestock Management: Strategies like rotational grazing and optimizing feed quality to reduce methane emissions.
CHALLENGES TO CARBON FARMING
- Geographical Variability:
- Effectiveness varies based on geographical location, such as long growing seasons, sufficient rainfall, and substantial irrigation being beneficial.
- Regions with adequate rainfall and fertile soil are more conducive to carbon sequestration through practices like agroforestry and conservation agriculture.
- Water Availability:
- Hot and dry areas with limited water availability pose challenges.
- Water scarcity can hinder plant growth and restrict carbon sequestration through photosynthesis.
- Practices like cover cropping may not be viable due to increased water demand.
- Plant Selection:
- Crucial to select plants that effectively trap and store carbon.
- Fast-growing trees and deep-rooted perennial grasses are better at carbon sequestration but may not thrive in arid environments.
- Financial Barriers:
- Adoption of carbon farming practices may require financial assistance for farmers.
- Small-scale farmers in developing countries like India may lack resources for sustainable land management practices and environmental services.
- Policy Support and Community Engagement:
- Sufficient policy support and community engagement are crucial for the success of carbon farming initiatives.
- Land management practices and community involvement play a significant role in the effectiveness of carbon farming.
GLOBAL INITIATIVES FOR CARBON FARMING
- Carbon Trading: Initiatives like the Chicago Climate Exchange and Carbon Farming Initiative in Australia incentivize carbon mitigation activities in agriculture.
- Agricultural Carbon Projects: Projects like Kenya’s Agricultural Carbon Project, supported by the World Bank, promote carbon farming in economically developing countries.
- ‘4 per 1000’ Initiative: A global initiative highlighting the role of carbon sinks in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.

